Europe has not yet taken stock of climate change. This is the message conveyed by the European Environment Agency in a report published at the start of the week.
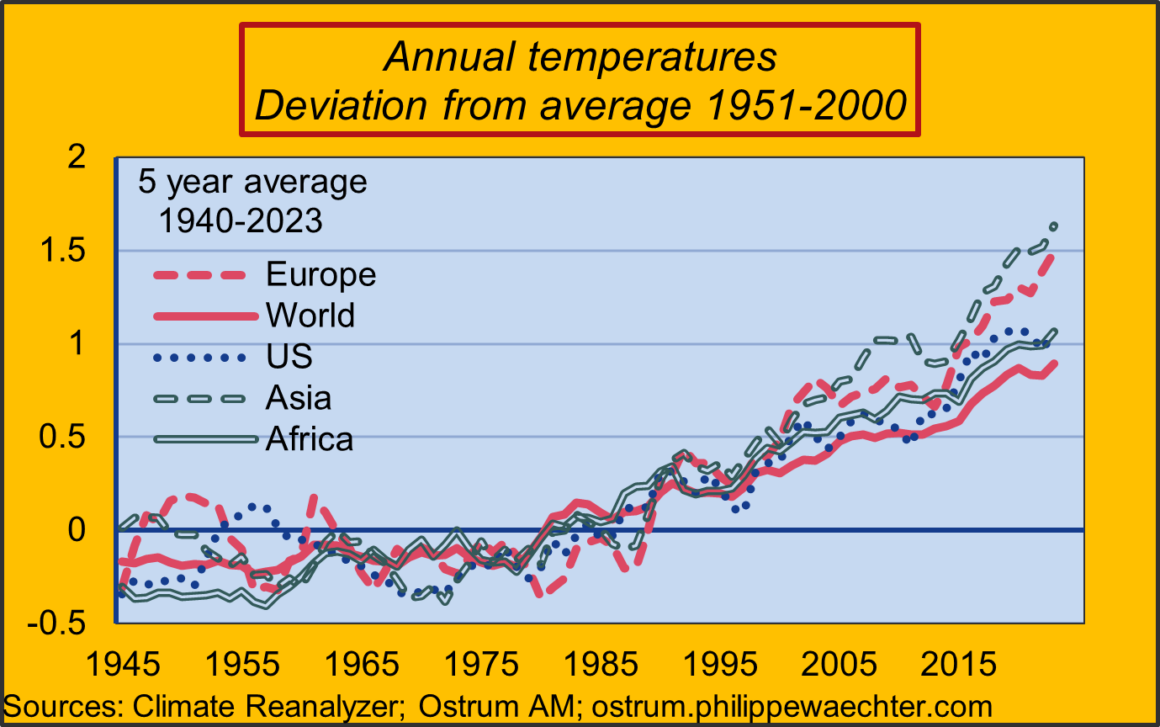
At comparable latitudes, Europe is the region that is warming the fastest. This is due to its geographical position and the sea currents of the Atlantic.
The graph is indicative of the acceleration in temperature in Europe since the start of the 2010 decade. In light of this intensification, we can better understand the new objective of the European Commission which wants to
The alert issued by the European Environment Agency (EEA) is of two types.
reduce carbon emissions by 90%, compared to 1990, by 2040 to take the risk of being carbon neutral in 2050.
The alert issued by the European Environment Agency (EEA) is of two types.
Europe is experiencing global warming and must prepare for an extreme scenario given the limited commitments of States on this issue. It will be permanently on a trajectory higher than that of the average global temperature.
This is a challenge in itself. This means more frequent climatic events. Periods of heatwave, like in 2022, of abundant rain, large-scale fires and more marked drought. Such occurrences have consequences on productive dynamics, whether industrial or agricultural. This situation can also result in higher deaths during periods of intense heat. The figure is estimated between 60,000 and 70,000 on a European scale.
The EEA emphasizes the persistent effect of these climatic events combined with ordinary shocks. The impact can be multiplied, have a greater impact in scale and duration than this ordinary shock taken in isolation
The Agency also emphasizes the fact that Europe being vast, the repercussions of climate bifurcation will not be uniform. Not all regions will experience the same types of climatic events with the same intensity.
- Productive, social and societal systems will have to adapt quickly to this new framework.
- Adjustment requests and support policies will need to be adapted. The framework, which was modulated by the history of each country within Europe, will have to be fundamentally altered to deal with the specificities resulting from the impact of climate change.
This could cause tensions between countries. We can take the example of water which will affect Europe due to periods of drought greater in intensity and duration. The countries of the South will be more penalized than those of the North, thus potentially being a major source of tensions between European countries.
It is then that European institutions will have to be solid and effective to contain its dissensions. Europeans must all move in the same direction and it will be the role of the Commission, Parliament and Governments to ensure this. Otherwise Europe risks quickly being destabilized by local particularities. This is one of the dimensions of the European elections next June.



